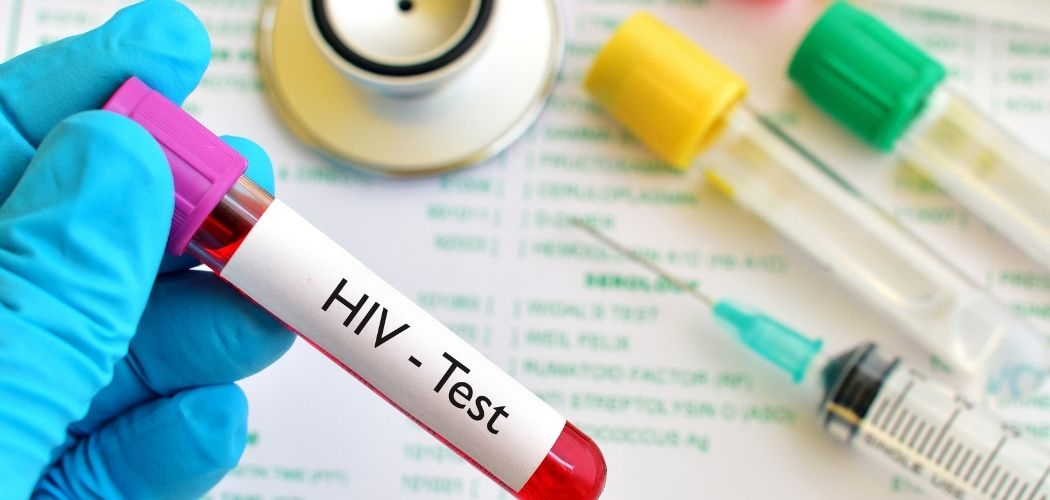
?AIDS is a disease that has a lot of history attached to it. There have been taboos in different societies about its origin and the people who suffer from it. While the estimated AIDS patients stand at 38 million, a high percentage of people are not aware of the disease or how to act around patients who are inflicted from it. Although, in the past two decades, awareness, screening tests, and proper ARTs have emerged as a hope for these patients, there is still a lot of ambiguity that surrounds the ailment.
What is AIDS?
AIDS is a debilitating disease caused by the RNA virus HIV. Human Immunodeficiency Virus attacks your immune cells and destroys them. These cells play a role in your body to protect it from innumerable germs like bacteria, fungi, viruses, parasites, and various foreign bodies. One must remember, HIV infection doesn't necessarily mean you have AIDS! It is referred to as AIDS only in severe cases when the immune cells become rare. AIDS patients usually die of one or more typical infections due to a poor immune system
Types of HIV
HIV is of two types-
- HIV Type I - It is the most common form plaguing countries worldwide. It spreads by sexual contact, blood transfusion, and via mothers to neonates.
- HIV type 2 - This variant is endemic to West Africa. The illness develops much slower due to this virus.
Individuals who think they have been exposed to the virus can undergo an HIV 1 & 2 antibodies screening test.
When to get tested?
HIV transmits via body fluids. Thus, situations that put you at high risk of HIV infection should qualify for a screening test. These include:
- Unprotected sexual contact with HIV patients
- Multiple sexual partners
- Blood transfusion from HIV patient
- Getting pricked from infected needles
- HIV positive mothers
- Drug abuse using infected needles
What are the HIV screening test types?
These are tests done to check whether you have the virus in your system. The screening tests are varied and give results after a specific window period. These tests allow better and early diagnosis that helps treatment. There are mainly three types of screening tests available. They are as follows:
Blood Test - A blood test detects the presence of antibodies in the serum. Antibodies are immune cells that develop in the body post-exposure to the infection. This test can detect antibodies 23-90 days after infection.
Antigen/Antibody Detection Test - The test helps to detect antigens and antibody detection in the patient's blood. These can detect HIV 18-45 days after exposure to the virus.
ELISA is an antigen/antibody detection test, very commonly used for accurate and early detection of HIV infection.
Rapid Test - These include rapid blood tests and rapid oral tests. A Rapid oral test requires the collection of oral fluid from between the teeth and gums. If you have had an infection for a while, these tests are highly accurate. While in the case of very recent ones, it might not be that reliable.
The test results come positive 23 to 90 days post-exposure. Rapid blood tests are easy to do at-home procedures. Just one finger prick and you can test for HIV infection. Even though it is as accurate as a lab-based test, the window period can extend from 18 to 90 days.
You can also use urine samples for HIV screening tests, but these tests are not as accurate as blood or oral fluids screening tests.
There are a few confirmatory tests that are undertaken after the screening test’s results come out positive to snub the idea of any false-positives. These include:
Western Blot Technique - The tests discussed above are screening tests used for diagnostic purposes. However, a western blot test is often undertaken to confirm the results.
Prognostic test - A nucleic acid test directly looks for the virus in the system. It does not detect antibodies. This means you are looking at a small window period of 10-33 days. A NAT test is expensive. Thus, they are recommended in cases of assured symptoms or to see the response to the treatment.
What is the procedure of screening tests?
HIV screening test procedure depends mainly on the sample being tested. For blood tests and antigen/antibody tests blood from a vein is collected. Rapid blood tests involve only a finger prick, and in the case of rapid oral tests oral fluid is collected using a spatula.
What do the test results indicate?
If you test positive for the screening tests for HIV 1 or HIV 2, it means you have the respective infection. This is confirmed by taking another blood test or confirmatory test. A screening test along with the confirmatory test is 99?curate.
- False-Positive- Sometimes patients can be tested positive even without having an infection. This may mostly occur in rapid tests. Therefore, these tests are followed by a blood test.
- False-Negative - Since HIV has a variable window period, tests examined during that time can be reported as a false negative.
Conclusion
The screening procedure and antiretroviral treatment have helped improve the lives of people suffering from HIV infection and AIDS. It is recommended by the Center for Disease Control that a person between 13-64 years should get tested at least once.
It is impressive that the accuracy of the tests is 90-100%. The fourth-generation tests have become very popular due to their accuracy and reliability. Thus, if you have doubts regarding exposure, you must get yourself screened!



 Login/Sign Up
Login/Sign Up